Discover 10 simple companion planting ideas to naturally deter pests, improve soil, & boost your vegetable garden harvests. Grow healthier plants with ease!
When it comes to organic vegetable gardening, mastering the concept of companion planting is a total game-changer. These “gardening buddies” are strategically grown together to enhance each other’s growth, naturally ward off pests, and even improve soil health.
Imagine boosting the overall vitality of your garden without relying on harsh pesticides. With these 10 simple companion planting ideas, you’re set for natural pest control and better, more bountiful harvests. Let’s get started!
(Posts on stacyling.com may contain affiliate links. Click HERE for full disclosure.)

What is Companion Planting?
Companion planting is a gardening technique where different plants are grown together for their mutually beneficial qualities. Certain plants have natural abilities to repel pests, attract pollinators, improve soil fertility, or provide shade and support to neighboring plants. By carefully selecting and arranging companion plants, you can create a thriving ecosystem in your vegetable garden and promote healthier plant growth.
6 Benefits of Using a Companion Plant Strategy
There are reasons you should incorporate companion planting in your vegetable garden.
- Natural pest control: Some companion plants have natural pest-repellent properties, helping to deter harmful insects and reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
- Improved pollination: Flowers of certain companion plants attract pollinators like bees and butterflies, ensuring better pollination for your vegetable crops.
- Weed suppression: Companion plants can help smother weeds by providing dense foliage, shading the soil, and preventing weed growth.
- Enhanced nutrient uptake: Some companion plants have deep roots that draw nutrients from lower soil layers, benefiting shallow-rooted vegetables by making those nutrients available in the upper layers.
- Soil improvement: Certain companion plants can improve soil fertility by fixing nitrogen or accumulating beneficial minerals.
- Increased yields: When companion plants work together harmoniously, they can lead to increased yields and healthier, more robust vegetable plants.

Companion Planting Tips For a Bountiful Veggie Patch
When practicing companion planting in your vegetable garden, it’s important to consider the specific requirements and characteristics of the plants you are growing. So always read those plant tags as it provides you with a wealth of information. Here are some guidelines to help you implement companion planting effectively.
Research and Plan
Before you start companion planting, research the compatibility and benefits of different plant combinations. Consider factors such as pest-repellent properties, nutrient requirements, growth habits, and flowering times (if any). Then plan your garden layout accordingly to maximize the benefits.
Complementary Companion Plant Pairings
Select companion plants that provide benefits to the neighboring vegetables. Look for plants that repel pests, attract beneficial insects, improve soil fertility, or offer shade and support. And aim for combinations where the strengths and weaknesses of each plant complement each other.
Proximity
In general, it’s best to plant companion plants in close proximity to the vegetables they are intended to protect. This allows for the exchange of beneficial compounds, such as scents and chemical signals. However, be mindful of not overcrowding the plants, as they still need adequate space to grow and access sunlight.
Spatial Considerations
Consider the growth habits and sizes of the plants involved. Taller plants like sunflowers or trellised crops can provide shade and support for shorter plants. Avoid planting tall companions that may overshadow or compete for resources with smaller vegetables.

Succession Planting
Take advantage of succession planting to ensure a continuous supply of companion plants throughout the growing season. And as one crop finishes, replant with another companion plant to maintain the benefits.
Observation and Adaptation
Observe your garden regularly and make adjustments as needed. Not all companion plant combinations will work equally well in every garden. Monitor for any signs of competition, nutrient deficiencies, or pest issues. If necessary, make changes to the layout or try different companion plant pairings.
Crop Rotation
Rotate your crops annually to avoid the buildup of pests or diseases that may affect both the vegetables and their companion plants. This helps maintain a healthy garden ecosystem and prevents long-term issues.
And it is a good idea not to plant in the same location within the same 3 to 4 years. Why? Because vegetables in the same botanical family are usually more susceptible to similar pests and diseases.
Therefore, home gardener should avoid planting them in the same location within 3 to 4 years. But waiting 5 years or more is even better if you have the growing space. So write down where you planted your vegetables too because trust me, you won’t remember next year!

10 Simple Companion Planting Ideas For Your Vegetable Garden
Now that you understand the benefits of partnering, let’s chat about these ten popular companion plant ideas and who they help in they pair well with.
Basil: The Flavor-Enhancing, Pest-Repelling Partner for Your Garden
Basil, a beloved herb in kitchens worldwide, is equally valuable in the vegetable patch. It’s not just for delicious pesto; this aromatic plant is a powerful ally for organic gardeners seeking to naturally enhance flavors and deter common garden pests.
Benefits of Planting Basil as a Companion
- Flavor Enhancement: Basil is famously believed to improve the flavor of nearby tomatoes and peppers, making your harvest even more delicious.
- Pest Deterrent: Its strong, pungent aroma acts as a natural repellent against a range of unwanted insects, helping to protect your precious crops.
- Beneficial Insect Attractor: When allowed to flower, basil can attract pollinators like bees and beneficial insects that prey on garden pests.
What Pests Does Basil Help Repel?
- Flies: The strong scent of basil can deter common flies.
- Mosquitoes: While not a primary garden pest, basil can help keep mosquitoes away from your gardening area.
- Tomato Hornworms: Some gardeners report that basil can help confuse or deter these large, destructive tomato pests.
- Thrips: There’s evidence that basil’s compounds can discourage thrips.

Best Vegetable Companions for Basil
Basil is an excellent neighbor for:
- Tomatoes: This classic pairing is legendary for both flavor enhancement and pest deterrence (especially for hornworms and flies). Plant basil close to your tomato plants.
- Peppers: Similar to tomatoes, basil is said to improve pepper flavor and offers pest protection.
- Asparagus: Basil can help deter asparagus beetles.
- Root Vegetables (Carrots, Beets, Onions): While less direct interaction, basil can contribute to overall garden health and deter general pests, benefiting these underground growers.
Avoid Planting Basil With
- Rue: This herb can stunt basil’s growth.
Zone 6 Gardener’s Tip: Basil thrives in the same warm conditions that tomatoes and peppers love, making it a perfect natural pairing for your zone 6b summer garden. For continuous pest deterrence and harvesting, consider succession planting basil every few weeks.
From My Garden to Your Table Basil Recipes
While basil is an excellent companion plant for tomatoes and other garden plants, it’s also great herb to grow for recipes! Some of my favorite ways to use my garden basil include:
- Basil Pesto Homemade
- Easy Bruschetta Tomatoes
- Best Recipe for Caprese Salad
- Caprese Salad Appetizer Bites

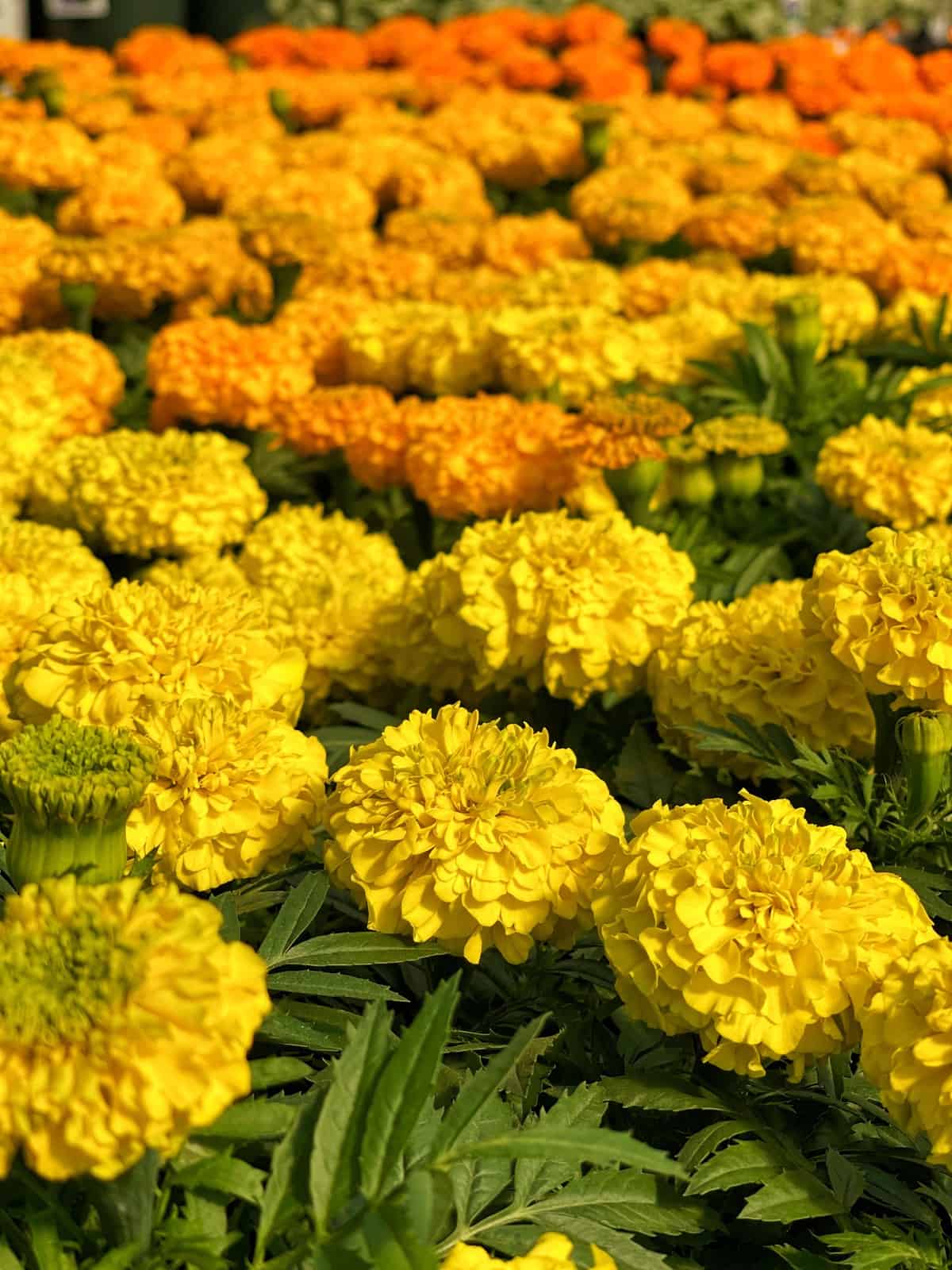
Marigold: Vibrant Pest Deterrents for Your Vegetable Garden
Marigolds (Tagetes spp.) are a classic companion plant, beloved by Bernardsville gardeners for their vibrant blooms and powerful pest-repelling abilities. Their strong scent acts as a natural deterrent, making them an invaluable partner for many common vegetable crops.
What Pests Do Marigolds Repel?
- Nematodes: Especially French Marigolds (Tagetes patula), are renowned for releasing compounds from their roots that suppress harmful nematodes in the soil, which can damage the roots of many vegetables.
- Aphids: The strong aroma of marigolds can help deter aphids from nearby plants.
- Whiteflies: Marigolds can also help to keep whiteflies at bay.
- Tomato Hornworms: Some gardeners find marigolds effective in repelling these notorious tomato pests.
- Mexican Bean Beetles: Certain varieties may deter these destructive bean pests.

Best Vegetable Companions for Marigolds
Marigolds are particularly beneficial when planted near:
- Tomatoes: To deter nematodes, whiteflies, and hornworms.
- Potatoes: For nematode control.
- Beans: To help repel bean beetles.
- Brassicas (Cabbage, Broccoli, Kale): Their strong scent can confuse pests.
- Squash and Cucumbers: Can help with squash bugs.
Tip for Zone 6 Gardeners: For optimal nematode control, plant French Marigolds as an annual cover crop or interplant them throughout your vegetable beds. Consider planting them early in the season to establish their root systems before pest populations peak.
I love marigolds for their companion planting capability, but also because they brighten up otherwise green spaces in my vegetable garden.

Nasturtiums: The Beautiful “Sacrificial Lamb” of Your Vegetable Garden
Nasturtiums, with their bright, edible flowers and peppery leaves, are far more than just a pretty face in the garden. For organic gardeners, they are an incredibly strategic companion plant, serving as a natural decoy and deterrent for common garden pests.
Benefits of Planting Nasturtiums as a Companion
- “Trap Crop” for Aphids: This is their most famous role! Nasturtiums are irresistible to aphids, drawing these sap-sucking pests away from your more valuable vegetable crops. They effectively become a “sacrificial lamb,” allowing you to manage aphid populations more easily.
- Pest Deterrent: Beyond aphids, their distinct scent and presence can discourage other troublesome insects.
- Edible & Versatile: Both the leaves and flowers are edible, adding a peppery zing to salads and garnishes – a bonus for any garden.
- Ground Cover & Moisture Retention: Their sprawling habit can help shade the soil, suppressing weeds and retaining moisture, especially beneficial in warmer Bernardsville summers.

What Pests Do Nasturtiums Help Repel or Trap?
- Aphids: Their primary target. Aphids flock to nasturtiums, leaving other plants alone. You can then easily hose them off the nasturtiums, or simply let nature take its course.
- Squash Bugs: Nasturtiums are known to deter these notorious pests of squash, pumpkins, and gourds.
- Cucumber Beetles: Their presence can help keep cucumber beetles away from your cucurbit crops.
- Whiteflies: Some gardeners find nasturtiums effective in reducing whitefly populations.
- Cabbage Worms/Loopers: The strong scent can sometimes confuse these brassica pests.
Best Vegetable Companions for Nasturtiums
Nasturtiums are particularly beneficial when planted near:
- Squash, Zucchini, Pumpkins: Excellent for deterring squash bugs and cucumber beetles. Plant them around the base of your squash plants.
- Cucumbers: Helps protect against cucumber beetles.
- Brassicas (Cabbage, Broccoli, Kale, Brussels Sprouts): Ideal for luring aphids away and potentially confusing cabbage worms.
- Radishes: Can help draw flea beetles away.
- Tomatoes: While not a primary pairing, they can offer general aphid deterrence for nearby plants.
Tips for Growing Nasturtiums in Your Garden
- Planting: Nasturtiums prefer full sun to partial shade and well-drained soil. Avoid overly rich soil, as this can lead to more foliage and fewer flowers.
- Management: Regularly check your nasturtiums for aphid buildup. Once they’re covered, you can decide to spray them off, or pull the plant if it’s too infested, to remove the pests from your garden.
Zone 6 Gardener’s Tip: Nasturtiums are relatively easy to grow from seed and thrive in my New Jersey summer conditions. Plant them strategically where you anticipate pest pressure, especially near squash and cucumbers, which are popular crops in my region. Their trailing varieties also make excellent companions in raised beds or hanging baskets.

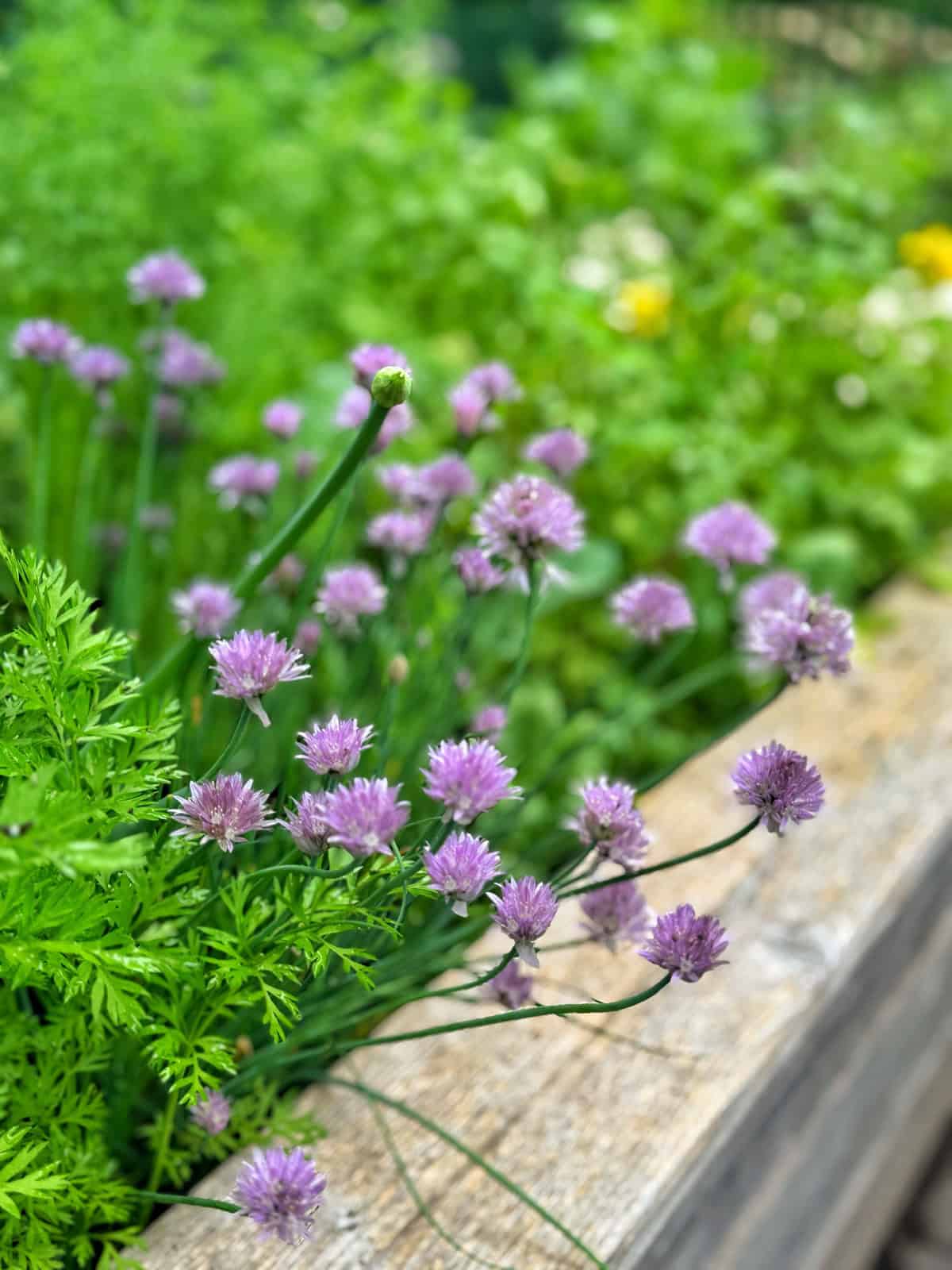
Chives: The Hardy Herb for Pest Protection & Flavor Enhancement
Chives, a member of the Allium family, are one of the easiest and most versatile herbs to grow in any garden. Beyond their culinary uses, their pungent aroma and resilient nature make them an exceptional companion plant, offering both pest deterrence and benefits to nearby crops.
Benefits of Planting Chives as a Companion
- Natural Pest Deterrent: Chives emit a strong scent that can confuse and repel a variety of common garden pests, helping to protect vulnerable plants.
- Disease Prevention: Their compounds can help deter fungal diseases like apple scab and black spot, making them beneficial even beyond the vegetable patch.
- Growth & Flavor Enhancement: Chives are known to improve the growth and flavor of specific nearby vegetables, particularly carrots.
- Beneficial Insect Attractor: When allowed to flower, their attractive purple blooms draw in pollinators like bees, as well as beneficial predatory insects (like hoverflies and parasitic wasps) that feed on garden pests.
What Pests Do Chives Help Repel?
- Aphids: The strong smell of chives helps to deter these ubiquitous sap-suckers.
- Carrot Rust Fly: A significant benefit for carrot growers, as chives can mask the scent of carrots, making them harder for the rust fly to locate.
- Japanese Beetles: Chives are reported to help deter these destructive beetles, a common challenge for gardeners in my region.
- Cabbage Worms: Their scent can confuse the moths that lay cabbage worms.
- Spider Mites: Some evidence suggests chives can help deter spider mites.
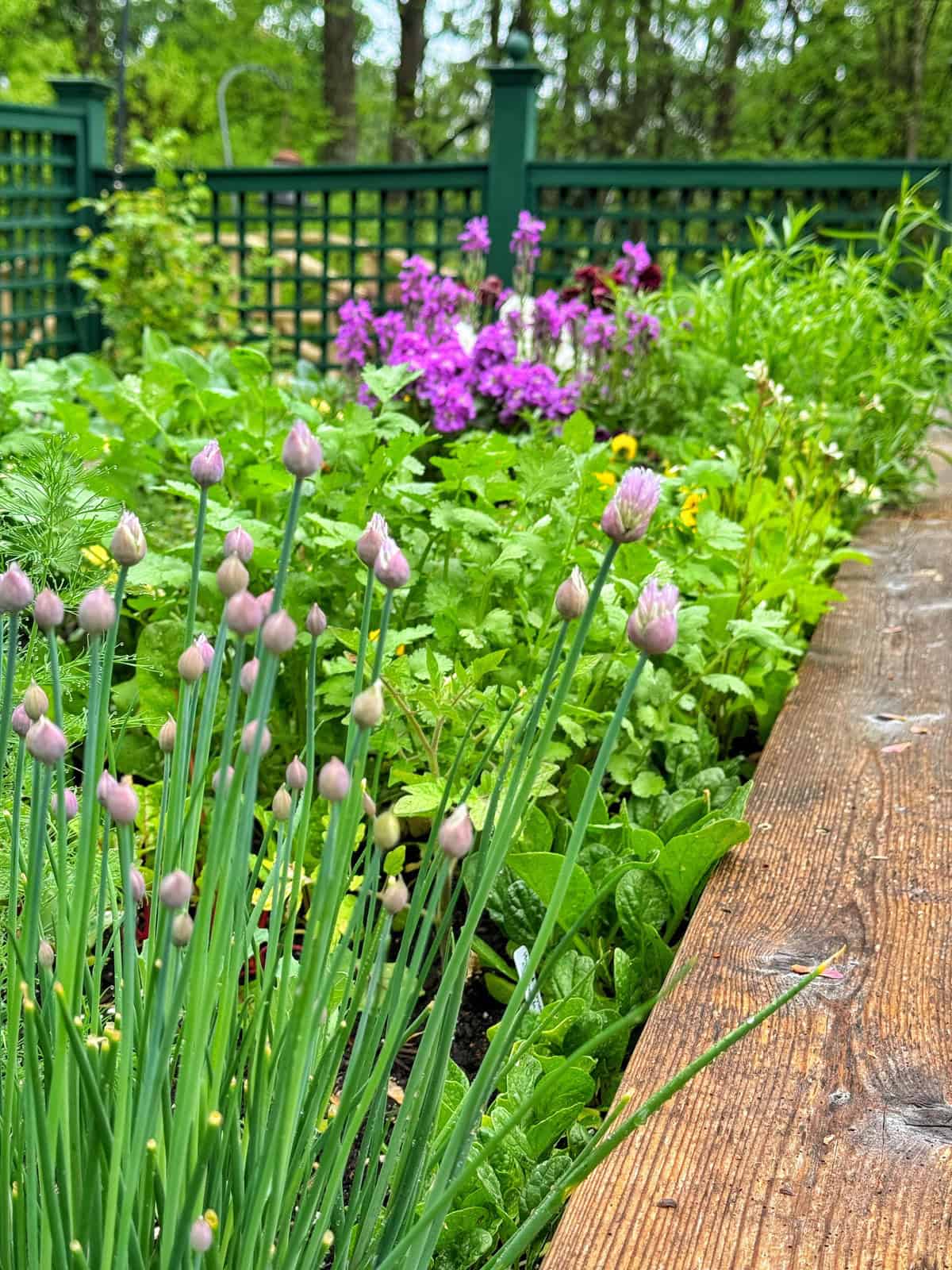

Best Vegetable Companions for Chives
Chives are excellent partners for:
- Carrots: The classic pairing, where chives are believed to enhance carrot growth and flavor, and crucially, repel the carrot rust fly. Plant them closely along your carrot rows.
- Tomatoes: Can help deter aphids and improve overall vigor.
- Rose Bushes: Historically used to deter aphids and black spot disease on roses.
- Apple Trees: Can help prevent apple scab.
- Brassicas (Cabbage, Broccoli, Kale): Their scent can help confuse cabbage worms and deter aphids.
- Lettuce & Other Leafy Greens: General pest deterrence for tender leaves.
Avoid Planting Chives With
- Beans & Peas: Like other alliums (onions, garlic), chives can inhibit the growth of beans and peas. This is due to compounds they release that can negatively impact the nitrogen-fixing bacteria on legum es.
Zone 6 Gardener’s Tip: Chives are incredibly cold-hardy, thriving through our Bernardsville winters and popping up early in spring. Consider planting them as a border around vegetable beds or directly interplanting with carrots. They are a low-maintenance powerhouse that can provide continuous harvest and pest control from early spring right through fall.
I plant chives to help repel aphids, Japanese beetles, and several other insects on my roses, raspberries, hardy hibiscus, and zinnias. They also attract pollinators and provide a lovely onion-like flavor to many dishes. While I tend to cut them often, I also LOVE the flowers. So I plant a few so I can get the best of both worlds.

Onions: The Pungent Protector for Your Vegetable Beds
Onions, a staple in kitchens and gardens alike, are more than just a root vegetable. As a powerful member of the Allium family, they bring robust pest-deterring capabilities to your organic vegetable garden. Their distinctive, pungent aroma is a natural repellent, making them an indispensable companion plant for home gardeners looking for effective, chemical-free pest control.
Key Benefits of Planting Onions as a Companion
- Broad-Spectrum Pest Deterrent: The strong sulfur compounds released by onions can confuse and repel a wide array of common garden pests, masking the scent of vulnerable crops.
- Disease Prevention: Similar to other alliums, onions can help deter certain fungal diseases, contributing to overall plant health.
- Soil Health: As they grow, onions can help loosen soil and improve its structure, benefiting nearby plants.
What Pests Do Onions Help Repel?
- Aphids: The strong smell is highly effective at keeping these common sap-suckers away from nearby plants.
- Cabbage Worms (Cabbage Loopers): Onions can confuse the moths that lay the eggs for these brassica-destroying caterpillars, making it harder for them to locate host plants.
- Carrot Rust Fly: A significant benefit for carrot growers! Onions help to mask the appealing scent of carrots, reducing carrot rust fly infestations.
- Slugs: While not a complete deterrent, their strong scent can make the area less appealing to slugs.
- Weevils: Some gardeners find onions helpful in deterring weevils from nearby crops.
- Japanese Beetles: While not their primary target, the strong scent can contribute to an environment less attractive to these pervasive pests, which are common in our region.

Best Vegetable Companions for Onions
Onions are excellent partners for:
- Carrots: This is a classic and highly effective pairing. Plant onions directly adjacent to carrot rows to maximize deterrence against the carrot rust fly.
- Brassicas (Cabbage, Broccoli, Kale, Brussels Sprouts): Ideal for protecting against cabbage worms and aphids. Interplant onions throughout your brassica patch.
- Lettuce: Their general pest-repelling qualities can benefit leafy greens.
- Beets: Onions can enhance the growth and flavor of beets.
- Tomatoes: Can help deter some general pests and improve overall vigor.
- Strawberries: Some gardeners find onions deter slugs and other pests from strawberry beds.
Avoid Planting Onions With
- Beans & Peas: As with other Alliums, onions can inhibit the growth of legumes due to compounds that can interfere with the nitrogen-fixing bacteria on their roots. Keep them separated for optimal yield.
- Asparagus: There is some debate, but many gardeners advise against planting onions near asparagus as they can both compete for nutrients and potentially inhibit each other’s growth.
Zone 6 Gardener’s Tip: Onions are a staple in many New Jersey vegetable gardens and are relatively easy to grow from sets or seeds. To maximize their pest-deterring effect, consider planting them in dense groups around the perimeter of vulnerable beds or intersperse them directly within rows of carrots or brassicas. For those planting in spring, ensure good drainage to prevent rot, especially after our typical wet spring weather.
Onions have a vertical growth habit, allowing you to maximize the use of garden space. You can interplant onions with other vegetables, utilizing the vertical space and effectively growing multiple crops in the same area. This helps optimize space and increase overall productivity in the vegetable garden. This is my first year growing onions. I can’t wait to harvest!

Borage: The Pollinator Magnet & Growth Enhancer for Your Garden
Borage, with its distinctive star-shaped blue flowers and fuzzy leaves, is not just a stunning ornamental; it’s a powerhouse companion plant. Known for its culinary and medicinal uses, this versatile herb truly shines in the organic vegetable garden by attracting crucial beneficial insects and supporting the health of nearby crops. For home gardeners, borage is an easy-to-grow annual that offers immense value from spring to frost.
Benefits of Planting Borage as a Companion
- Exceptional Pollinator Attractor: Borage flowers are a magnet for bees (including native bees), butterflies, and other vital pollinators. This is critical for improving the fruit set and yield of many vegetable crops.
- Beneficial Insect Host: Its blooms also attract predatory insects like parasitic wasps and hoverflies, which are natural enemies of common garden pests such as aphids and tomato hornworms.
- Flavor and Growth Enhancement: Borage is traditionally believed to improve the flavor and overall growth of certain vegetables, most notably strawberries and tomatoes.
- Soil Health: As a deep-rooted plant, borage can draw up nutrients from deeper in the soil, making them available to shallower-rooted plants when its leaves decompose (acting as a “dynamic accumulator”).
- Deterrent for Tomato Hornworms: Its presence is thought to deter these large, destructive pests from tomato plants.

What Pests Does Borage Help Deter or Control?
- Tomato Hornworms: Borage is particularly renowned for its ability to repel or confuse these major tomato pests.
- Cabbage Worms: Its strong scent can help deter cabbage worms from brassica crops.
- Aphids: By attracting aphid predators like hoverflies and ladybugs, borage helps to naturally control aphid populations.
Best Vegetable Companions for Borage
Borage is an outstanding partner for:
- Tomatoes: The most classic pairing! Borage is believed to improve tomato flavor and vigor while deterring hornworms. Plant it interspersed among your tomato plants.
- Strawberries: Said to enhance both the flavor and yield of strawberries, and potentially help deter certain berry pests.
- Squash & Cucumbers: Borage attracts the pollinators essential for good fruit set in these cucurbit crops. Its deterring qualities can also help with squash bugs.
- Cabbage & Other Brassicas: Can help repel cabbage worms and attract beneficial insects that prey on brassica pests.
- Fruit Trees (especially Apple Trees): Often planted beneath fruit trees to attract pollinators and deter codling moths.
Tips for Growing Borage in Your Garden
- Sowing: Borage is easily grown from seed directly sown in your garden after the last frost. It readily self-seeds, so be prepared for new plants to emerge next season!
- Location: Plant borage in full sun to partial shade. Its sprawling habit means it needs some space.
- Maintenance: Allow some flowers to go to seed for self-seeding, or deadhead regularly for continuous blooming.
Zone 6 Gardener’s Tip: Borage thrives in the sunny conditions of my New Jersey summers and its rapid growth makes it a quick provider of benefits. It’s a fantastic choice for attracting a diverse range of pollinators to your garden, crucial for our local fruit trees and vegetable crops. Its self-seeding nature means you’ll likely have it return year after year, establishing a beneficial presence with minimal effort.
Whenever the Japanese beetles arrive, they flock to my borage plants and generally staying off my other plants. So I consider borage a good trap crop to help protect plants from Japanese beetle damage.

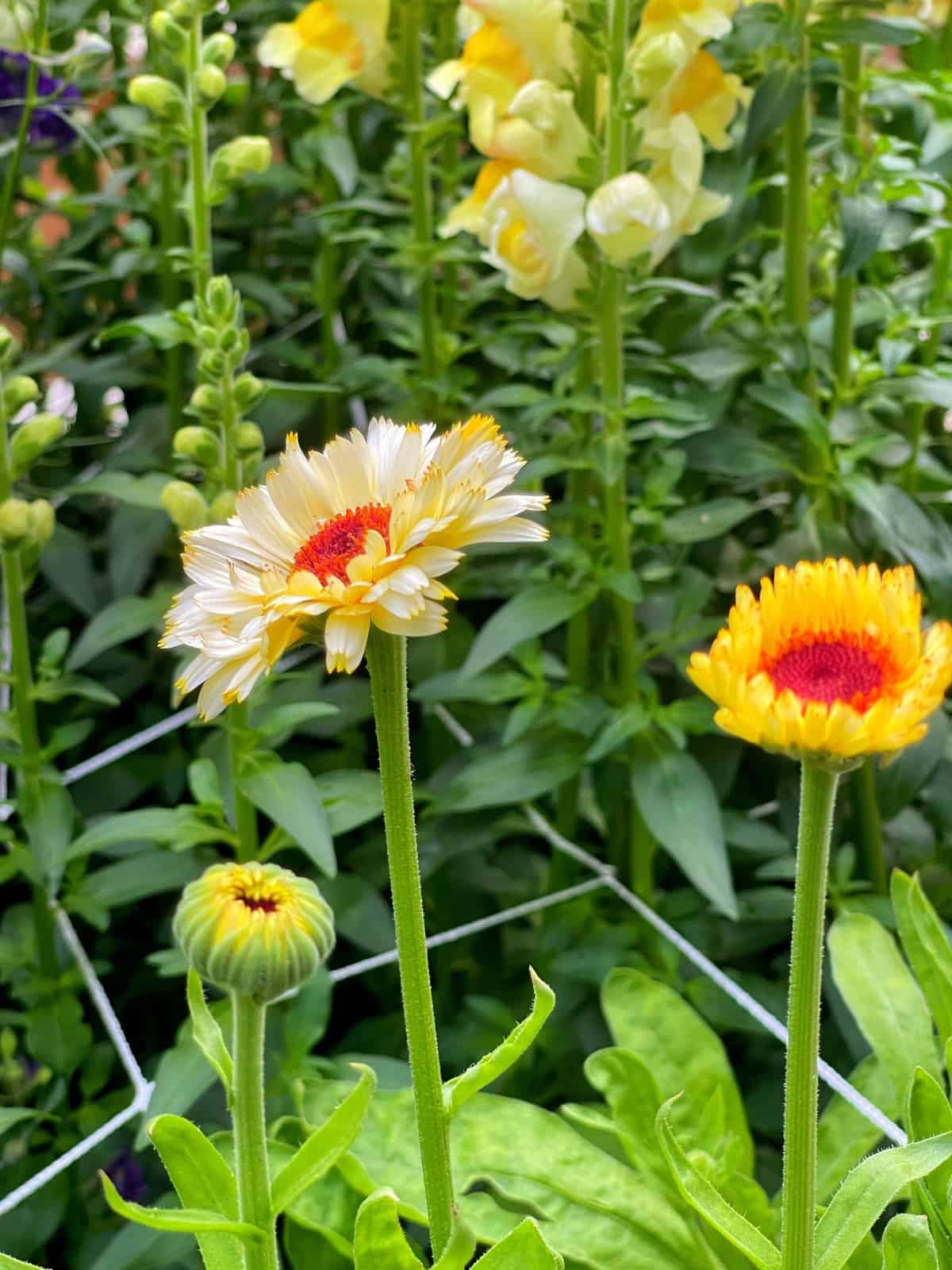
Calendula (Pot Marigold): The Golden Ally for a Pest-Free Garden
Calendula, often known as “Pot Marigold” (though distinct from French or African marigolds), is a brilliant, cheerful annual that brings a splash of golden-orange to any garden. For organic gardeners, this easy-to-grow flower is an invaluable companion plant, offering a range of benefits from attracting beneficial insects to deterring specific pests, all while adding edible beauty.
Benefits of Planting Calendula as a Companion
- Exceptional Beneficial Insect Attractor: Calendula’s open, accessible flowers are highly attractive to a wide array of beneficial insects, including:
- Ladybugs: Voracious predators of aphids.
- Hoverflies: Their larvae are effective aphid eaters.
- Lacewings: Also known for preying on aphids and other soft-bodied insects.
- Pollinators: Attracts bees and butterflies, aiding in the pollination of nearby vegetable crops.
- Pest Deterrent: While primarily known for attracting predators, calendula also has a reputation for directly deterring certain pests.
- Edible Flowers: The vibrant petals are edible and can add color and a mild peppery flavor to salads, soups, or as a garnish.
- Soil Nematode Suppression (Limited): Some studies suggest certain varieties may have a limited effect on specific types of nematodes, though less potent than true Marigolds (Tagetes spp.).
- “Trap Crop”: Occasionally, calendula may attract aphids, acting as a minor trap crop to draw them away from more valuable plants.
What Pests Does Calendula Help Deter or Control?
- Aphids: Indirectly, by attracting their natural predators (ladybugs, hoverflies, lacewings) which then control aphid populations.
- Asparagus Beetles: Calendula is specifically noted for its ability to deter these common pests of asparagus.
- Tomato Hornworms: Its presence is believed to help deter or confuse these large, destructive tomato pests.
- Nematodes: While not a primary function like Tagetes marigolds, some varieties may offer minor nematode suppression in the soil.

Best Vegetable Companions for Calendula
Calendula is an excellent partner for:
- Asparagus: A classic pairing, helping to deter the problematic asparagus beetle. Plant calendula near your asparagus beds.
- Tomatoes: Believed to deter tomato hornworms and generally enhance the garden’s ecosystem for healthier tomato growth.
- Brassicas (Cabbage, Broccoli, Kale, Brussels Sprouts): By attracting aphid predators, calendula helps protect these aphid-prone crops.
- Leafy Greens (Lettuce, Spinach): General benefits from increased beneficial insect activity.
- Beans & Peas: Can help deter some pests and attract beneficials.
Tips for Growing Calendula in Your Garden
- Sowing: Calendula is very easy to grow from seed, either direct-sown in early spring or started indoors. It often self-seeds readily.
- Sunlight: Prefers full sun but can tolerate partial shade, especially in hotter climates.
- Deadheading: Regularly deadhead spent blooms to encourage continuous flowering throughout the season, which maximizes its attraction for beneficial insects.
Zone 6 Gardener’s Tip: Calendula is a robust annual that thrives in the varied summer conditions of New Jersey. Its continuous blooming from late spring through frost makes it a consistent source of beneficial insect activity for your garden. Consider planting them as a cheerful border or intersperse them directly within your vegetable beds, particularly near asparagus, which is a popular perennial crop in our area.
Plus, calendula’s bright and vibrant flowers are a magnet for pollinators, including bees and butterflies. The abundant nectar and pollen-rich blooms attract these important pollinators like butterflies to your garden. Increased pollinator activity can result in improved pollination for your vegetable plants, leading to better yields and fruit set.
I’ve been growing calendula for a few years now. They start with ease from seed but the critters love them. So keep an eye on seed starts. I lost an entire crop last year from a rabbit.

Dill: The Feathery Herb for Beneficial Bug Recruitment
Dill, with its delicate, feathery foliage and distinctive anise-like aroma, is a culinary favorite that doubles as an outstanding companion plant in the organic vegetable garden. Known for its ability to attract a diverse array of beneficial insects, it’s a strategic asset for home gardeners looking to enhance natural pest control and boost garden biodiversity.
Benefits of Planting Dill as a Companion
- Exceptional Beneficial Insect Attractor: Dill’s flat, umbrella-like flower heads (umbels) are particularly appealing to a wide range of beneficial insects when allowed to bloom:
- Ladybugs: Their larvae are voracious predators of aphids.
- Lacewings: Generalist predators of aphids, mites, and other soft-bodied insects.
- Parasitic Wasps: Crucial for controlling caterpillars like cabbage worms and tomato hornworms.
- Hoverflies: Larvae feed on aphids; adults are pollinators.
- Pollinators: Attracts bees and other pollinators, improving fruit set on nearby crops.
- Host Plant for Swallowtail Butterflies: Dill is a preferred host plant for the caterpillars of beautiful Black Swallowtail butterflies, adding an aesthetic and ecological benefit to your garden.
- Pest Deterrent (Limited): While primarily an attractor of predators, its strong scent can also subtly deter certain pests from vulnerable crops.
What Pests Does Dill Help Control?
- Cabbage Worms (Cabbage Loopers): By attracting parasitic wasps, dill helps significantly reduce populations of these brassica pests.
- Aphids: Indirectly controlled by the presence of ladybugs, lacewings, and hoverfly larvae.
- Tomato Hornworms: Parasitic wasps attracted to dill can help parasitize hornworm larvae.

Best Vegetable Companions for Dill
Dill is an excellent partner for:
- Brassicas (Cabbage, Broccoli, Kale, Brussels Sprouts): A classic pairing. Plant dill nearby to attract the beneficial insects that prey on cabbage worms and aphids, protecting your cruciferous crops.
- Lettuce & Other Leafy Greens: Can help deter general pests and enhance overall garden health.
- Cucumbers: Attracts pollinators, which are vital for cucumber fruit set.
- Corn: Can help deter spider mites and attract beneficials.
- Onions: No direct benefit, but they generally coexist well.
Avoid Planting Dill With
- Carrots: Dill can inhibit the growth and vigor of carrots, potentially stunting their root development. Keep a good distance between these two crops.
- Tomatoes: While some sources suggest benefits, others indicate dill can inhibit tomato growth. It’s often best to plant it a short distance away from tomatoes or focus on other companions for them.
- Fennel: As both are members of the Apiaceae family, they can cross-pollinate and potentially produce hybrid seeds. They can also compete for resources and attract similar pests.
Zone 6 Gardener’s Tip: Dill is a robust, self-seeding annual that thrives in the full sun of New Jersey summers. Allow some plants to go to seed to ensure its return year after year, providing continuous beneficial insect attraction. Plant dill strategically near your brassica beds for maximum effect against cabbage worms, a common challenge in our area’s vegetable gardens.
When dill starts to bolt, let it flower. It’s a great host plant for butterflies as they like to lay their caterpillar eggs on them.

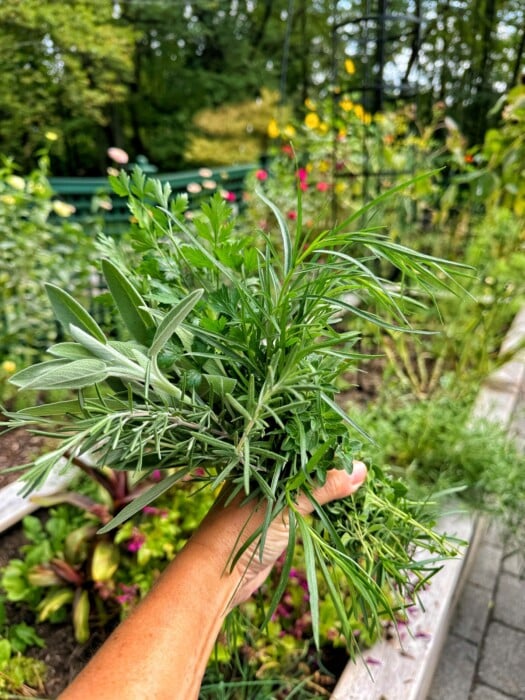
Sage: The Aromatic Shield for Your Vegetable Patch
Sage, a highly aromatic and resilient herb, is a cornerstone of both culinary traditions and effective organic companion planting. Its distinctive, earthy scent is a powerful deterrent for a range of garden pests, making it an invaluable addition to any vegetable garden, especially for home growers seeking natural pest management solutions.
Key Benefits of Planting Sage as a Companion
- Potent Pest Deterrent: The strong fragrance of sage effectively masks the scent of vulnerable crops, confusing and repelling insects that rely on smell to find their host plants.
- Natural Insecticide Properties: Beyond deterrence, sage contains compounds that can have insecticidal effects on certain pests.
- Beneficial for Specific Herb Growth: Known to enhance the growth and vigor of certain neighboring herbs.
- Repels Slugs: The texture and scent of sage can also make it unappealing to slugs and snails.
What Pests Does Sage Help Repel?
- Cabbage Moths (Cabbage Worms/Loopers): Sage is highly effective at deterring the adult cabbage moths, preventing them from laying eggs that hatch into destructive cabbage worms on your brassicas.
- Carrot Rust Fly: Its strong aroma helps to mask the scent of carrots, making them harder for this damaging fly to locate.
- Fleas: Can help deter fleas from pets or surrounding areas if planted strategically.
- Slugs & Snails: The texture and strong scent of sage leaves are generally disliked by these mollusks.
- Some Aphid Species: While not a primary deterrent for all aphids, its scent can contribute to an overall less hospitable environment.
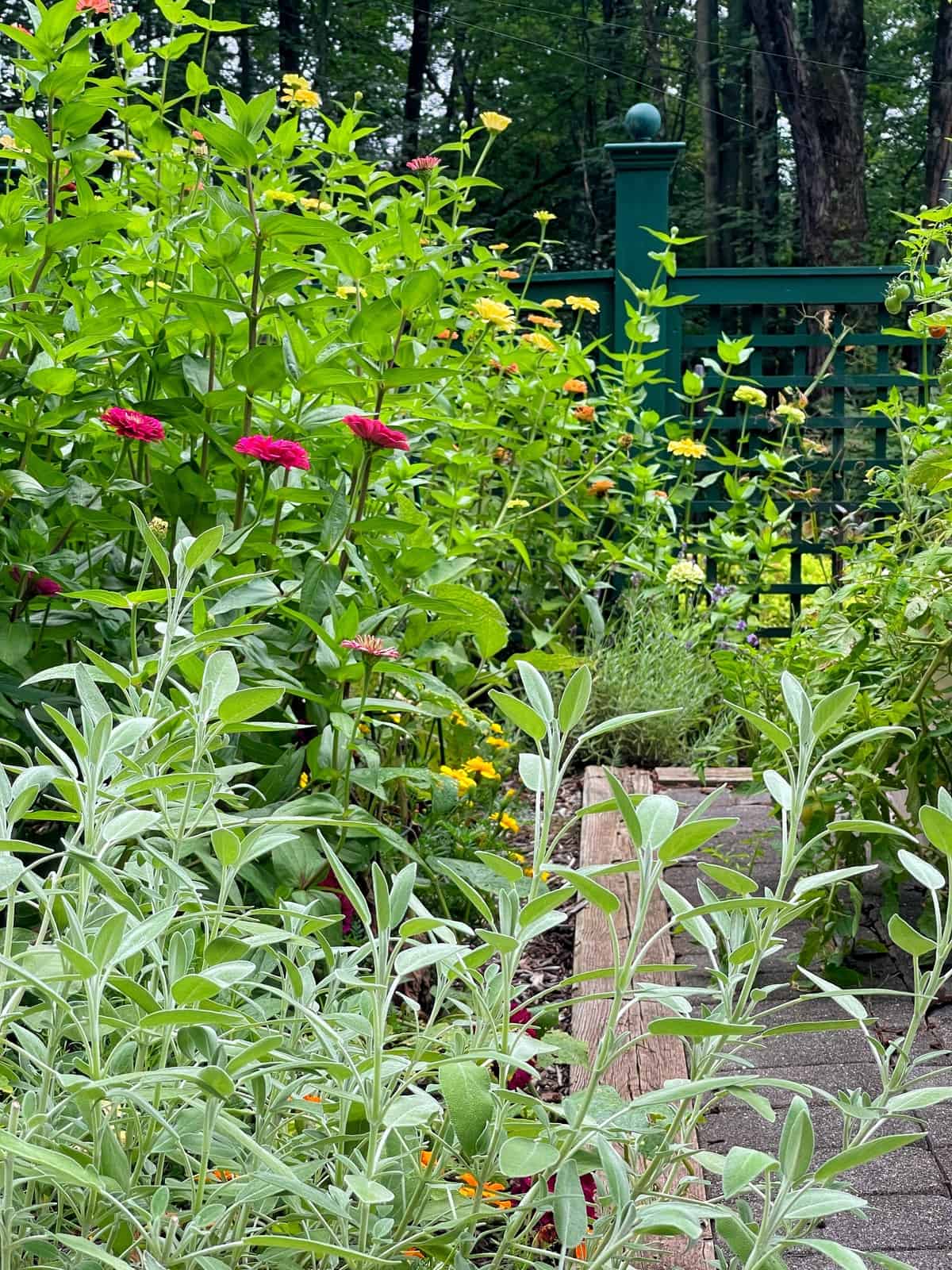

Best Vegetable Companions for Sage
Sage is an excellent partner for:
- Brassicas (Cabbage, Broccoli, Kale, Brussels Sprouts): A classic and highly effective pairing for deterring cabbage moths and preventing cabbage worm infestations. Plant sage near or around your brassica beds.
- Carrots: Plant alongside carrot rows to help deter the carrot rust fly.
- Rosemary: Sage is known to mutually benefit rosemary, enhancing its growth.
- Strawberries: Can help deter slugs and some other pests from berry patches.
- Tomatoes: While not a primary pairing, some gardeners find sage can offer general deterrence against certain pests when interplanted.
Avoid Planting Sage With
- Cucumbers: Sage is believed to inhibit the growth and flavor of cucumbers.
- Onions: Like other members of the mint family, sage can sometimes inhibit the growth of alliums like onions.
- Rue: The strong compounds in rue can negatively affect sage’s growth.
Zone 6 Gardener’s Tip: Sage is a hardy perennial herb that thrives in the varied climate of New Jersey returning reliably year after year. It prefers full sun and well-drained soil. Consider planting sage as a living border around your brassica beds or near your carrot patch for continuous, natural pest protection. Its beautiful foliage and drought tolerance once established make it a low-maintenance, high-impact addition to your local garden.
It also enhances the flavor of many vegetables when used in cooking. Do you grow it? It’s really easy to grow and is perennial in certain growing zones.

Rosemary: The Fragrant Protector for Your Vegetable Beds
Rosemary, with its pine-like fragrance and evergreen foliage, is a highly versatile and beloved herb, equally prized in the kitchen and the garden. As a robust companion plant, its potent aroma acts as a powerful natural deterrent for a range of common garden pests, making it an indispensable addition for organic gardeners seeking effective, low-maintenance pest solutions.
Benefits of Planting Rosemary as a Companion
- Powerful Pest Deterrent: The strong, camphoraceous scent of rosemary effectively confuses and repels insects that rely on their sense of smell to locate host plants, masking the aroma of vulnerable crops.
- Attracts Pollinators: When it blooms, rosemary’s small blue flowers attract bees and other beneficial pollinators, which can improve fruit set on nearby vegetables.
- Evergreen Structure: As a woody perennial in many climates, it provides year-round structure and a continuous source of pest deterrence.
- Companion for Herbs: Known to enhance the growth and vigor of certain nearby herbs, particularly sage.
What Pests Does Rosemary Help Repel?
- Cabbage Moths (Cabbage Worms/Loopers): Rosemary is highly effective at deterring the adult moths, preventing them from laying eggs on your brassica crops.
- Bean Beetles: Its strong aroma helps to repel these destructive pests from bean plants.
- Carrot Rust Fly: The scent of rosemary can mask the smell of carrots, making it difficult for the carrot rust fly to find them.
- Slugs & Snails: The texture and strong scent of rosemary leaves are generally unappealing to these mollusks.
- Flea Beetles: Can help deter flea beetles from certain crops.

Best Vegetable Companions for Rosemary
Rosemary is an excellent partner for:
- Beans: A classic pairing, as rosemary helps to repel bean beetles, which can devastate bean crops. Plant rosemary near your bean rows.
- Carrots: Plant alongside carrot rows to deter the carrot rust fly, especially beneficial for spring-planted carrots.
- Brassicas (Cabbage, Broccoli, Kale, Brussels Sprouts): Highly effective at keeping cabbage moths away, significantly reducing cabbage worm damage. Interplant or place rosemary strategically around your brassica patch.
- Sage: Rosemary is believed to benefit from being planted near sage, enhancing both herbs’ growth.
- Thyme: They share similar growing conditions and can mutually benefit.
Avoid Planting Rosemary With
- Mint: While both are herbs, mint’s aggressive spreading habit can quickly overwhelm rosemary and compete for nutrients. Plant mint in containers.
- Basil: Rosemary prefers drier conditions than basil, which thrives with more moisture. Their needs conflict.
- Potatoes: Some gardeners report that rosemary can inhibit potato growth.
Zone 6 Gardener’s Tip: In New Jersey, rosemary is often grown as an annual or overwintered indoors, as it can be marginally hardy in our Zone 6b winters, especially if exposed to harsh winds. For best results, choose a sunny, well-drained spot. Planting it near your spring and summer vegetable crops like beans and brassicas will provide continuous protection throughout the main growing season, which is well underway by mid-June. If you plant it in a container, you can easily bring it inside when colder weather arrives.


Final Thoughts About Companion Planting for Your Veggie Garden
These are just a few examples of companion plants that can protect specific vegetables. Keep in mind that the effectiveness of companion planting may vary depending on various factors, such as your specific region, garden conditions, and pest populations. So it is not an exact science.
It’s always a good idea to experiment and observe how companion plants interact with your vegetables to find the combinations that work best for your garden.
Happy gardening!
For more information about companion planting in your vegetable garden, please see this article from the University of Minnesota Cooperative Extension.
Do you have companion plants you regularly use? What companion pairings work well for you? I would love to know more in the comments below.
To drill down on more beginner gardening techniques and tips, please read these posts:
- Flower Gardening 101
- Growing a Cut Flower Garden for Beginners
- Container Garden Ideas for Beginners
- How to Start a Vegetable Garden
- Herb Gardening for Beginners
Thank you for visiting the blog today!
Enjoy your day! xo